KML is a type of file format used to display geographic data. GoogleEarth uses this type of format when displaying their maps of the Earth. Remote sensing is used to produce these files. Remote sensing is a technique used to collect data about the Earth without taking a physical sample of the Earth's surface. This is done by placing a sensor to measure the energy from the sun reflected from the earth. This information obtained can be displayed as a digital image or as a photograph.
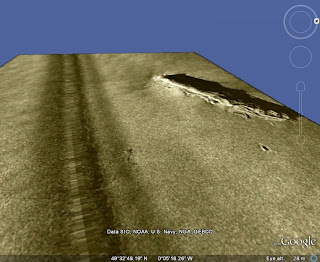
This example of a KML image was taken from a sunken French submarine off the coast of Europe. The image was credited to the US Navy and is taken from an Eye alt of 28 meters.